Yarrow
-
By
 YaserFoods
YaserFoods
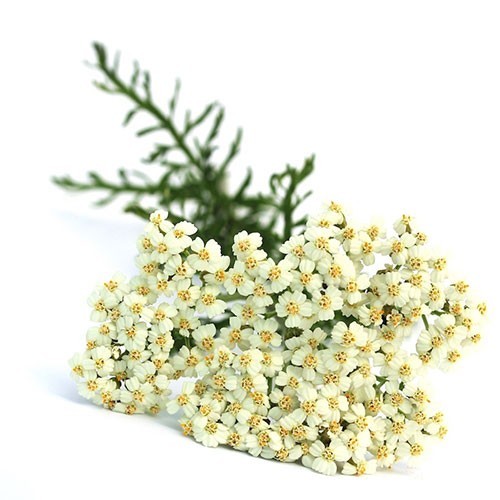
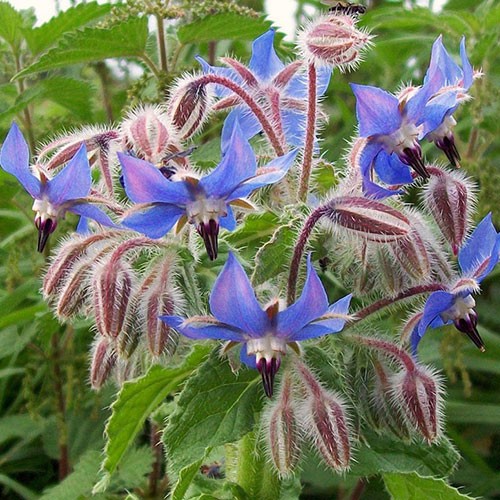
Yarrow
Scientific name: Achillea millefolium
English name: Yarraow, Nosebleed, Sanguinary, thousand leaf
Farsi name: Boomadaran, Boomadaran hezarbarg, Berenjasf, Ghisoom
Arabic name: Hazbal, Em alf vargha
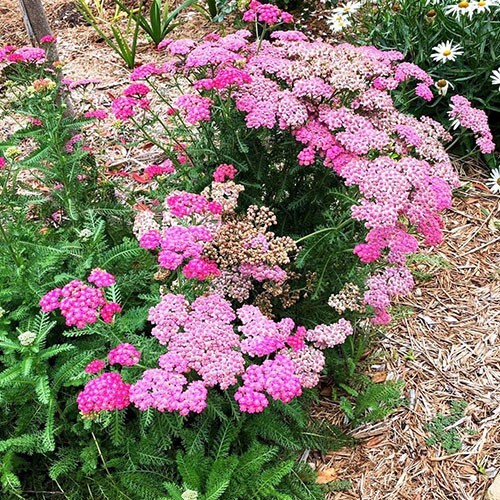
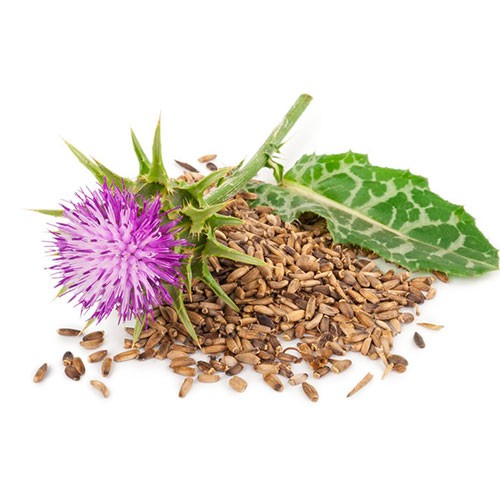
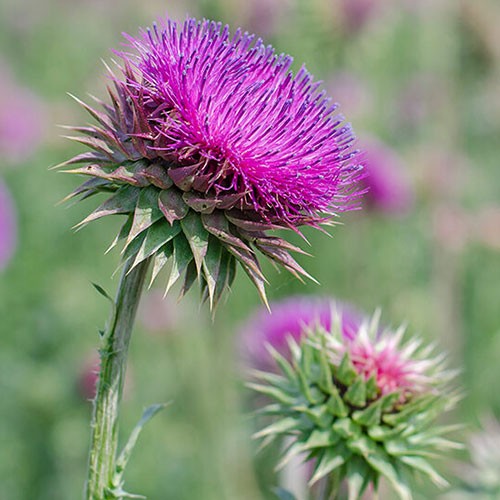
Yarrow belongs to the Asteraceae family and medicinal organs of this plant are its flowers, stems and leaves. The height of this plant is 1-2 meters with simple, erect stems and spear-shaped leaves and white, pink or purple fragrant flowers. Yarrow usually grows in early spring.
The Latin name of this plant is derived from the name of Achilles, the legendary hero of Greece. According to Studies, around 1200 BC, yarrow was used to treat wounds and prevent bleeding and infection.
Yarrow plant with high medicinal properties is used in the treatment of many diseases.
• flu treatment
• Relieve anxiety
• Improves the digestive system
• Treatment of hypertension
• Treatment of stomach and gastrointestinal disorders
• Treatment of irregular menstruation
• Treatment of infection and mastitis
• Regulate blood pressure
• Asthma treatment
• flu treatment
Yarrow plant has compounds such as, Flavonoids, Fatty acids, Protein, Tocopherol, Iron, Phosphorus, Sulfur, essential oil, Camphor, Sineol, Caryophylline, AlphaPen, Isoarthritis, Polyenes contain ponticapoxide and others.
Yarrow is a kind of hardy plant that can live in harsh environments and grows naturally in plains, roadsides and mountainous areas. it grows wild throughout the Northern Hemisphere and originally belongs to Europe, Western Asia, the Mediterranean and most parts of Iran.